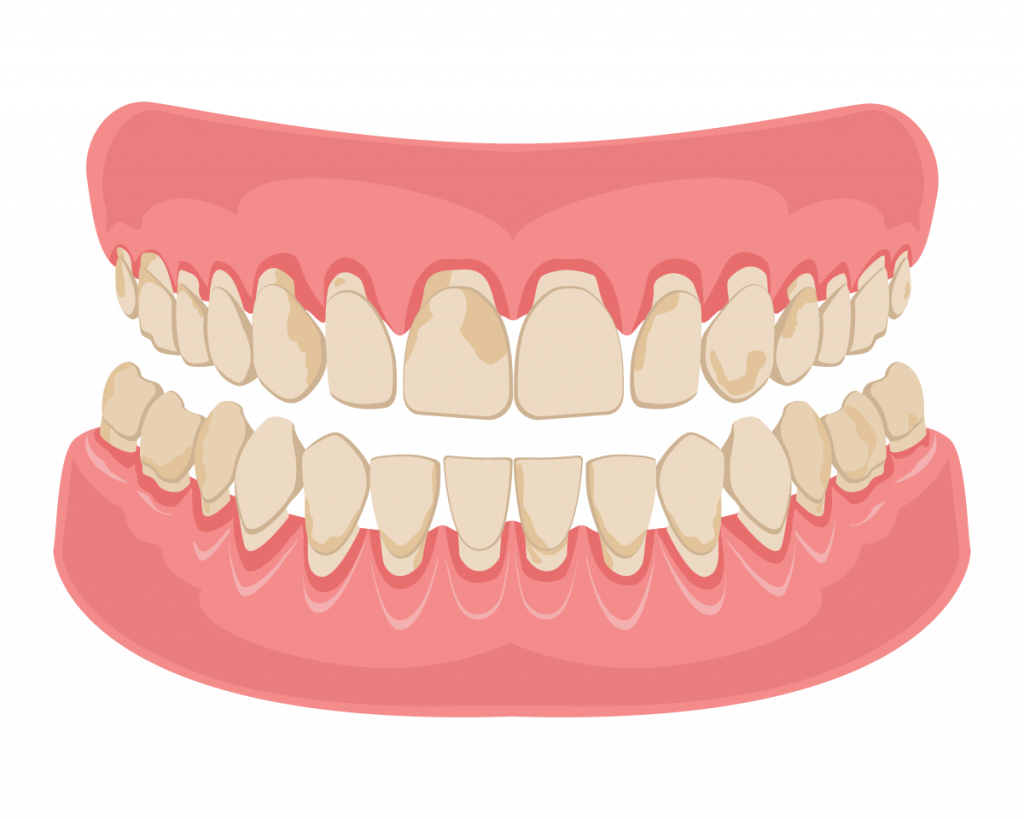
What is periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a severe and destructive infection of the gums and surrounding tissues of the teeth. Periodontitis can progress to destroy the gum and the supporting jawbone. This can lead to teeth mobility and eventual tooth loss. However, the good news is that periodontitis can be treated, and all its ugly complications can be avoided with prompt treatment.
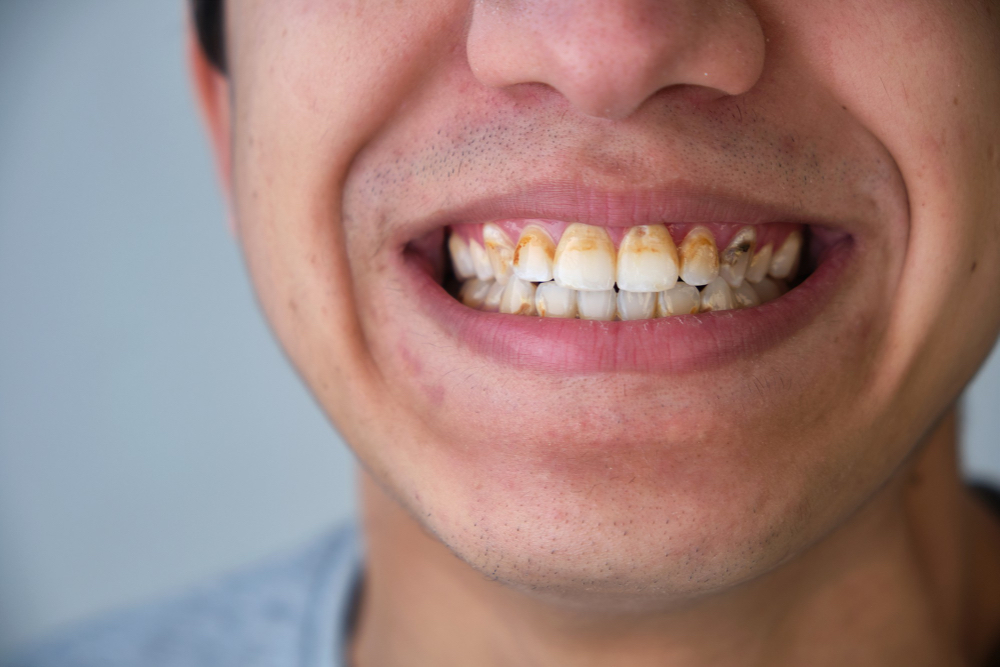

What causes periodontitis?
The leading cause of periodontitis is bacteria-laden plaque. Plaque is a sticky yellowish film inhabiting bacteria that firmly adheres to the tooth structure and the gums. These bacteria metabolise the sugars from the food we consume and release acidic substances into the oral cavity. These bacterial by-products are toxic and generate an inflammatory response in the gums, which leads to gum diseases like periodontitis.
The plaque, if not removed, hardens and calcifies with time to form calculus which is even more adherent and cannot be removed by regular oral hygiene methods. It can even accumulate beneath the gum line, where it wreaks havoc on the supporting teeth structures.
What are the stages of periodontitis?
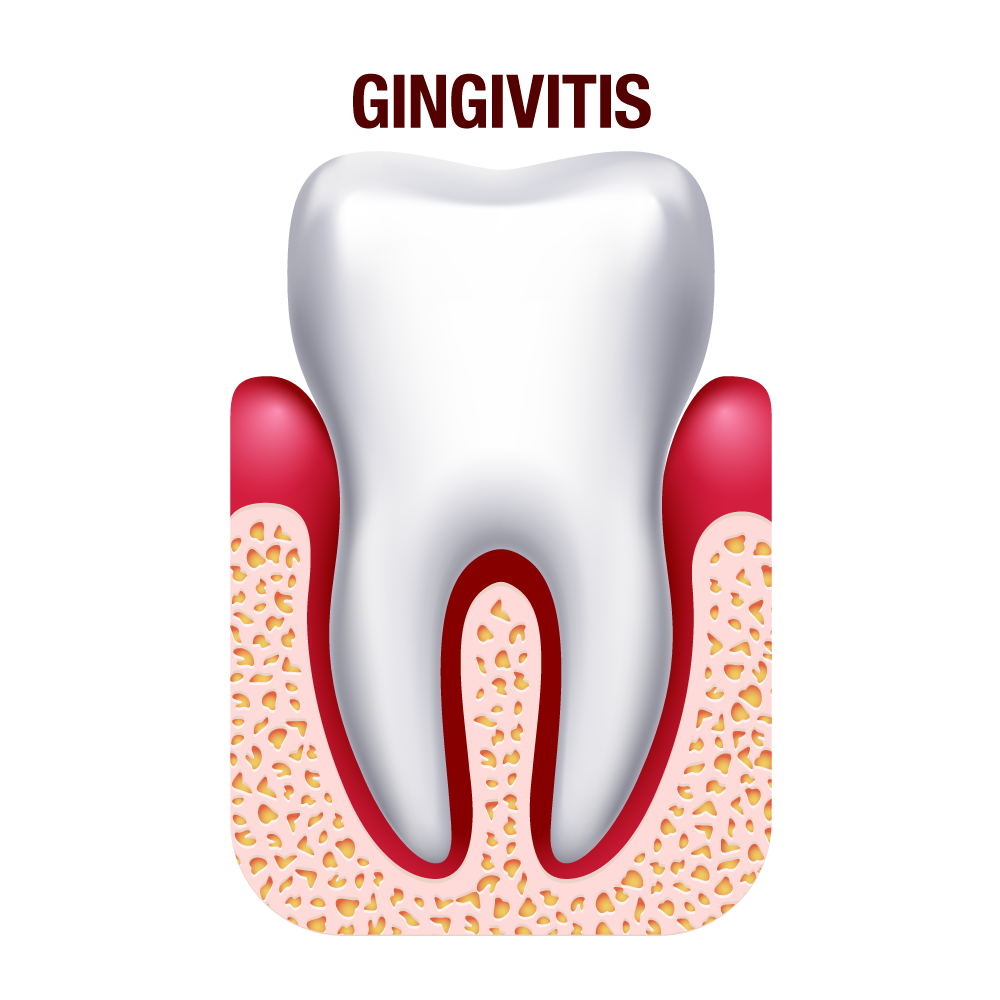
Stage 1- Inflammation (gingivitis)
The first stage of periodontitis is inflammation. Inflammation of the gums is known as gingivitis. Gingivitis is a mild and non-destructive form of gum disease which leads to swollen and fiery red gums. If the infection is not controlled at this stage, it can progress.
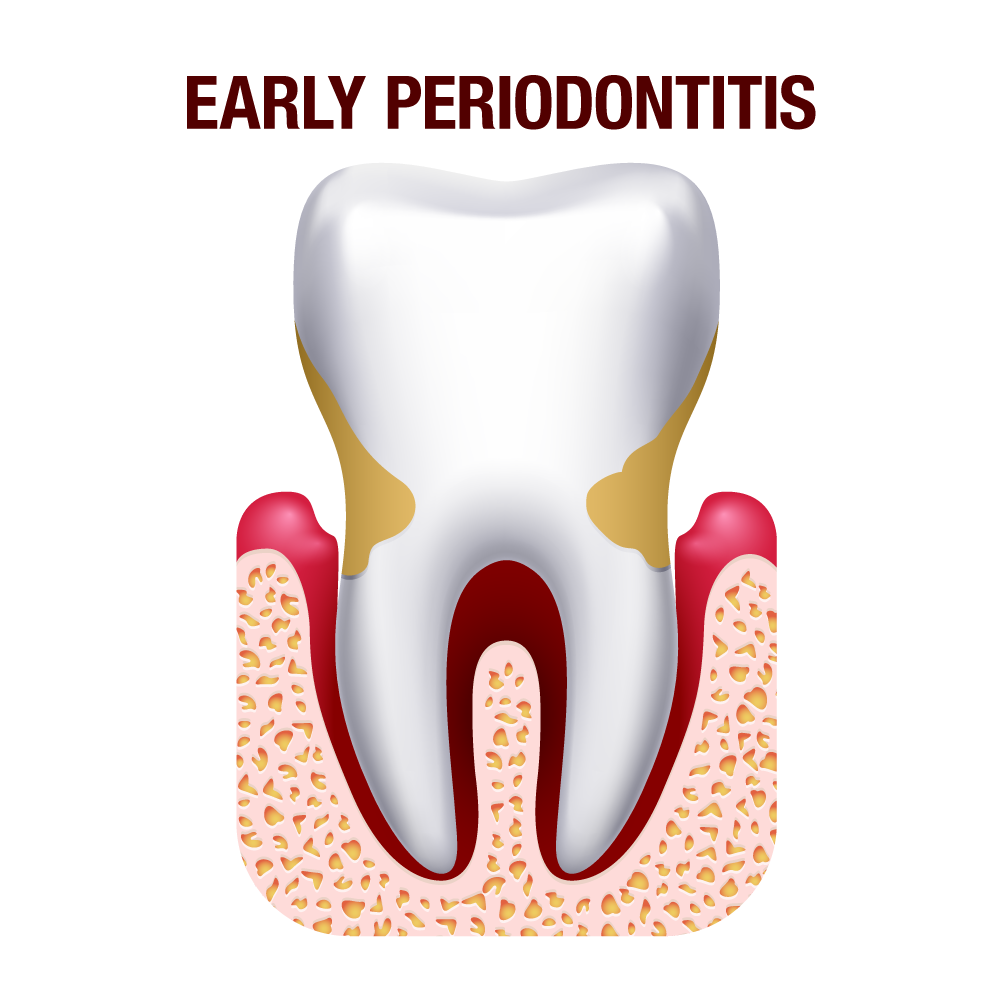
Stage 2- Early periodontitis
The bacterial infection progress, and it is known as early periodontitis. In this stage, the inflammation advances and starts destroying the biological integrity of the gums. As a result, the gums begin to pull away from the teeth leading to gum recession. You may also notice pocket formation in the gums. As the gums pull away from the teeth, a gap is formed between the tooth and gum line. You may also notice some bleeding from gums during brushing and flossing.
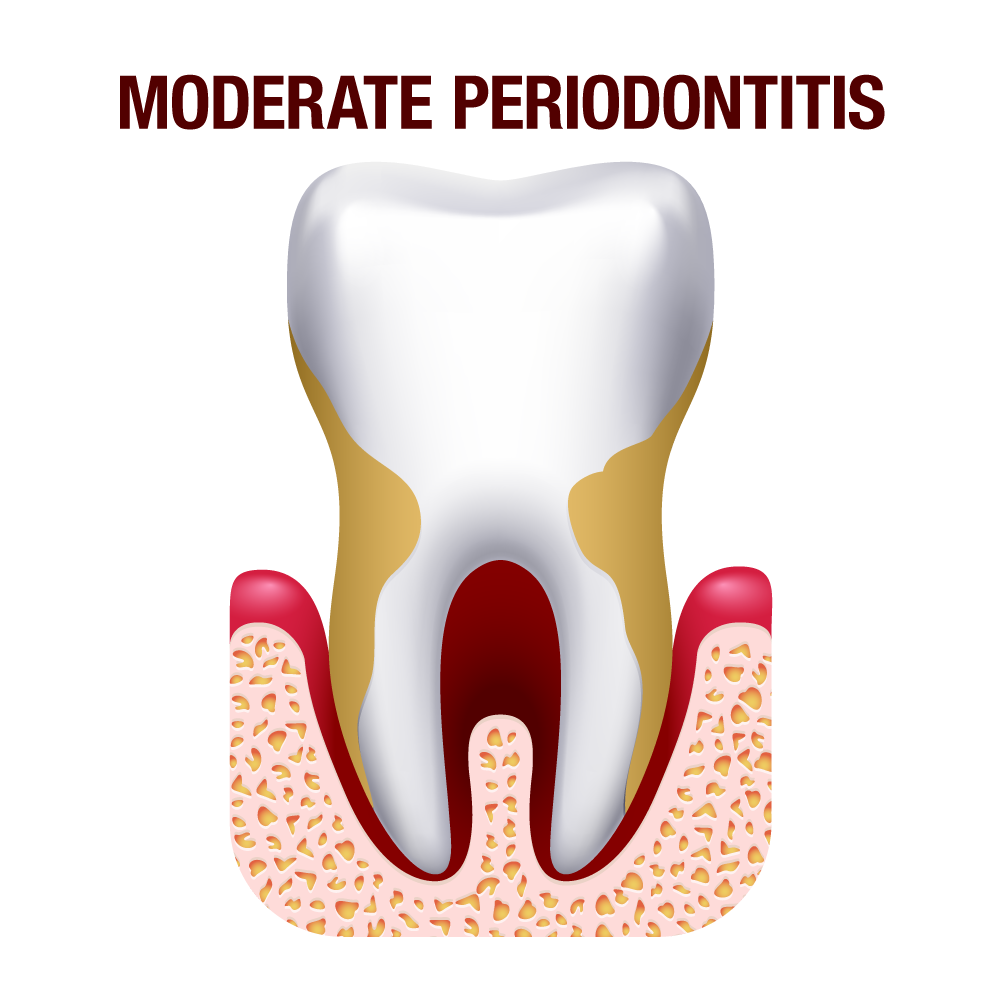
Stage 3 – Moderate periodontitis
If the infection is allowed to progress, it leads to moderate periodontitis. During this stage, the bone supporting the teeth is affected, and its destruction begins. The gums and bone are destroyed, and gum recession and pocket formation increase. The gums appear fiery red and may lead to pain. Due to the destruction of the jaw bone and other teeth supporting structures, the teeth become mobile.
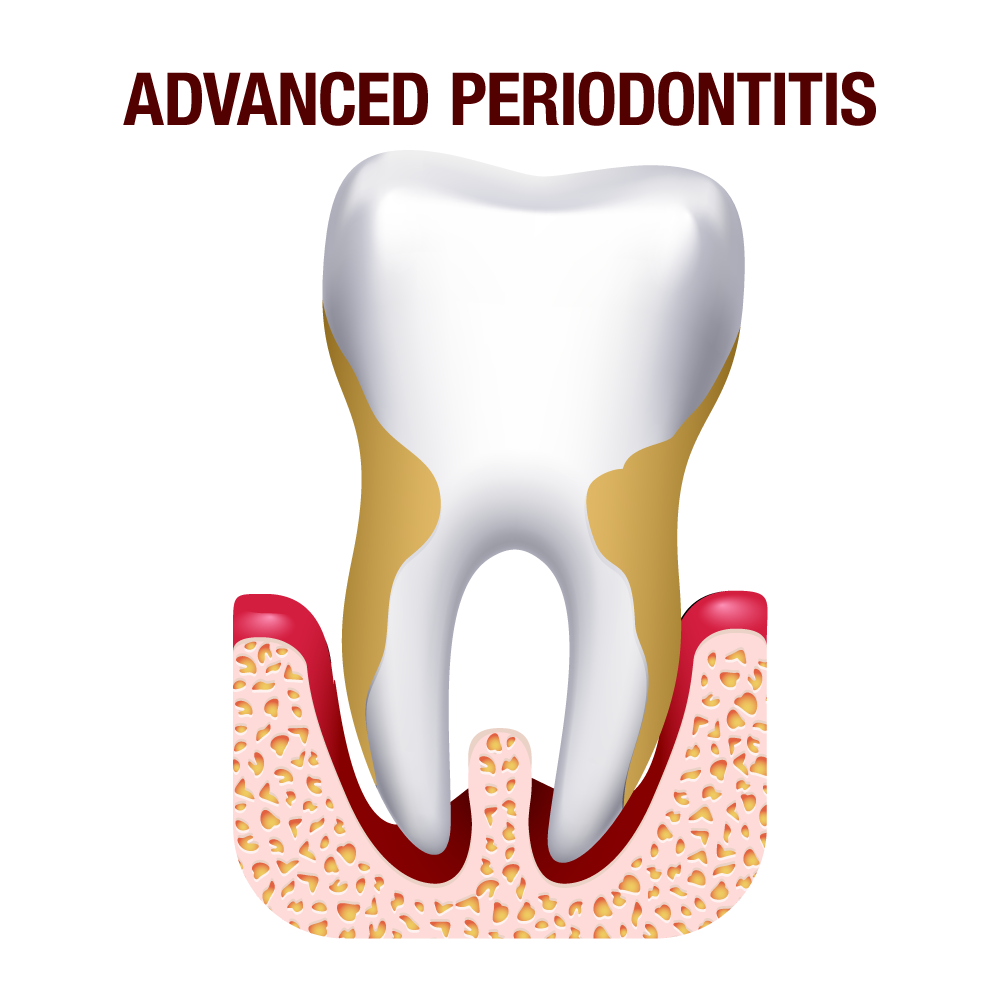
Stage 4 – Advanced periodontitis
This is the last and most severe stage of periodontitis. The infection has progressed and destroyed the gums and bones to cause irreversible damage. The bone support is lost, teeth become exceptionally mobile and will eventually fall off. This may also be accompanied by pus discharge from the gumline, a foul taste and bad breath. The damage is too extensive; it may require comprehensive surgical intervention to treat the condition and restore gum health.
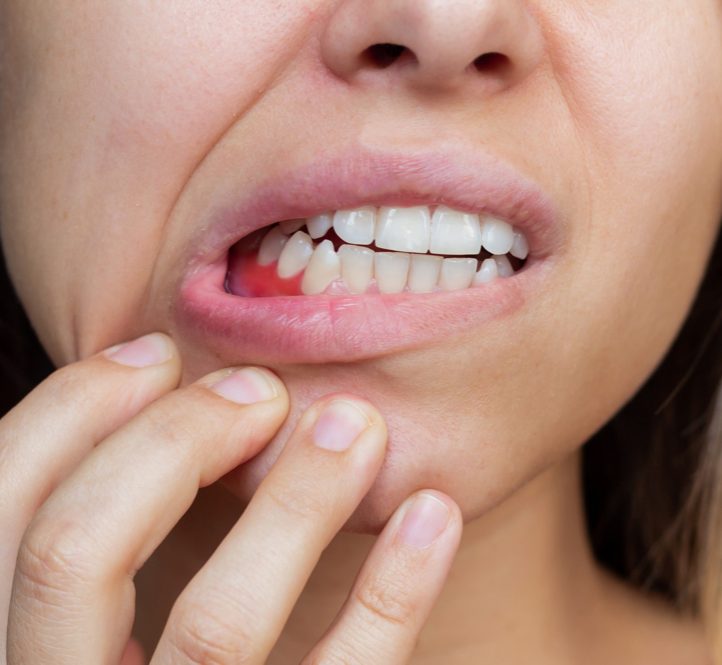
Symptoms of periodontitis
Symptoms of early stages of periodontitis may not be very noticeable. Owing to this, many people don’t seek treatment at early stages and report to our dental clinic after the infection has advanced. Symptoms of periodontitis vary according to the various stages of disease but generally the symptoms maybe –
- Swelling of the gums which may be localised to few teeth or may involve the entire jaw.
- Bleeding from gums upon brushing and flossing. Sometimes, it can even occur while chewing.
- Bad breath and a metallic foul taste in the mouth.
- Receding gum.
- The position of the teeth can change, accompanied by teeth mobility.
- Fiery red and painful gums.
- Plaque and tartar accumulation.
- Pain while chewing.
- Eventual tooth loss.
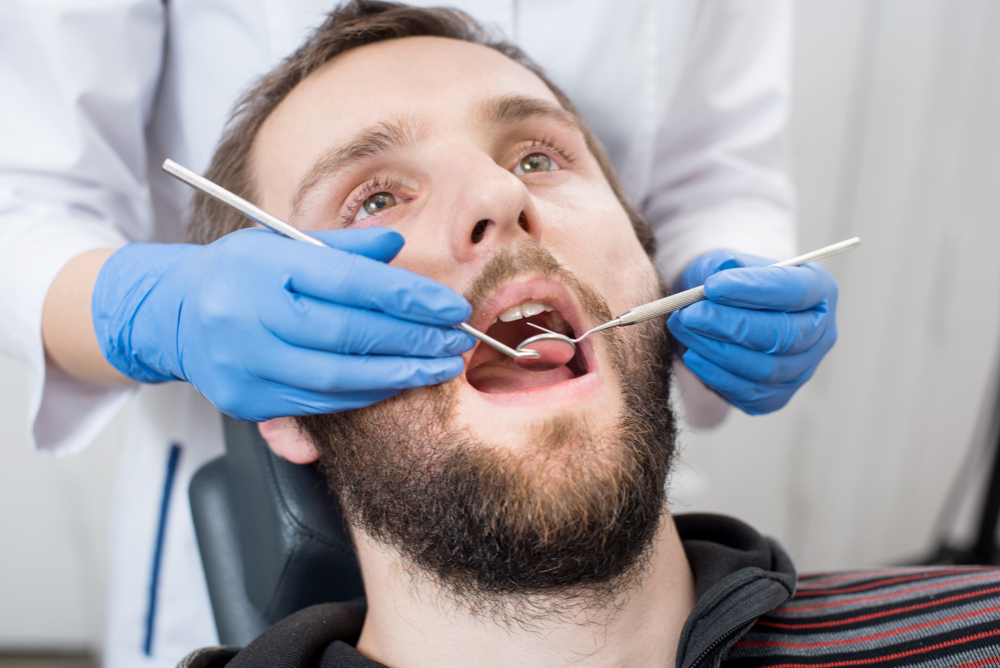
Diagnosis of periodontitis
Our dentist will diagnose periodontitis based on clinical signs and symptoms. They may also probe your gums to check for pocket, degree of gum recession and bleeding. In addition, they may order some x-rays and OPG to visualise the full extent of the damage.
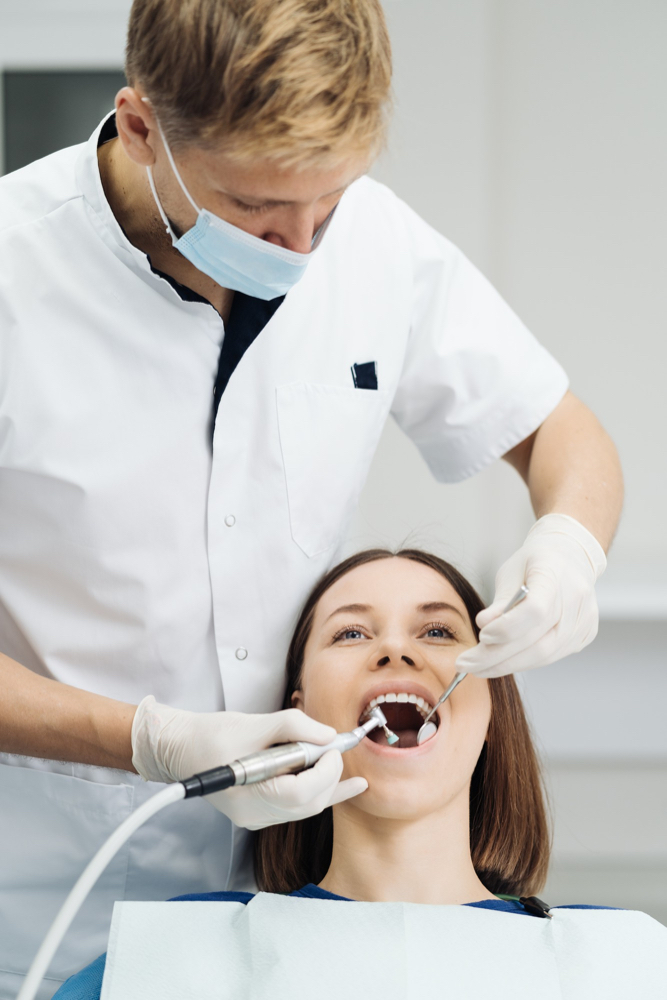
Treatment of periodontitis
Treatment of periodontitis comprises deep cleaning, infection control through medication and if required, bone regenerating and gum revival surgeries.
Initially, our dentist will carry out thorough scaling and root planning. This reduces the bacterial load and allows the gums to heal. They may also put you on antibiotics to help infection control and also prescribe a medicated chlorohexidine mouthwash.
You will be called for follow-ups where the improvement of your oral health will be assessed. In some cases of advanced periodontitis, the tooth becomes so mobile that there is no other option left but to extract them.
After analysing the effects of primary care, they will decide if you need an additional procedure to establish the gum height. They may also advise you to undergo bone grafting procedures to regenerate the lost bone.
Apart from this, they will instruct you on proper oral health care practices. Having a good oral hygiene routine is imperative to maintaining oral health and ensuring that the gums are not reinfected.

What are the possible complications of periodontitis?
Untreated periodontitis can lead to extreme teeth mobility and eventual teeth loss. In addition, bacteria from the gums can enter the bloodstream and affect other organs leading to sepsis.
Moreover, it is seen that people with diabetes face more severe consequences of periodontitis and could lose all their teeth at an early age. Through extensive research, it has also been shown that periodontitis could derange the sugar levels in diabetic patients be a cause of uncontrolled diabetes.

Prevention of periodontitis
As with every dental disease, the best way to prevent periodontitis is to have a proper oral hygiene routine. Use a soft-bristled nylon toothbrush and ensure you are covering every tooth surface. In addition to this, keep your tongue clean and remember to floss each day.
Eat nutritious, healthy foods and restrict consumption of sugary drinks and chewy, sticky candies. Apart from this, schedule a dental appointment with us at least once every six months. This allows our dentist to catch the gum disease at its initial stages, treat them and prevent it from progressing.
If you have any more questions or would like to schedule a dental check-up, call us, and our team of exceptional dental professionals will be there to help you towards better oral health.
